Gum Surgery | Everything About Treating Gum Diseases and Gum Recession
Gum surgery is one of the advanced dental procedures used to treat gum issues, such as advanced gum diseases or gum recession. This surgery helps restore gum tissue, improve oral and dental health, and prevent more serious problems. In this article, we explore the types of gum surgery, benefits, drawbacks, and recovery process, using information from reliable sources like Cleveland Clinic, Medical News Today, and Colgate.
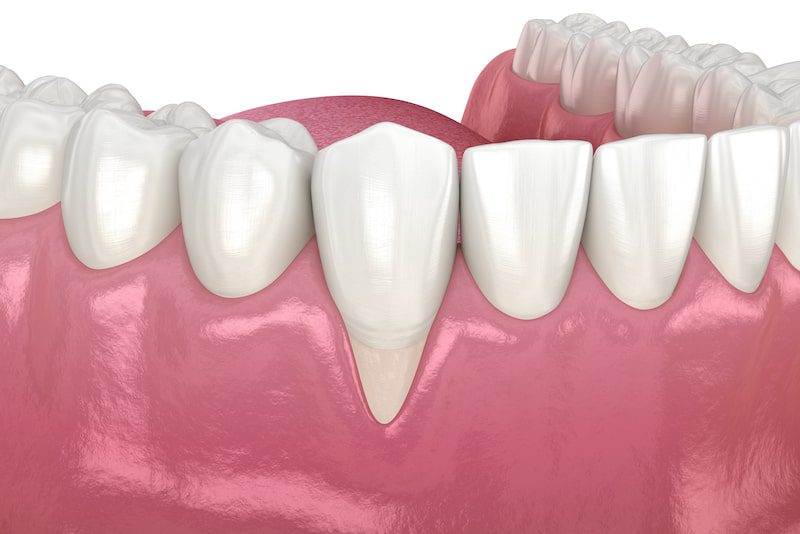
What is Gum Surgery?
Gum surgery is a treatment method aimed at improving gum health and addressing issues such as gum recession, gum diseases (periodontitis), and severe infections. Typically performed by a periodontist, gum surgery involves various techniques tailored to the patient’s needs.
Reasons for Gum Surgery:
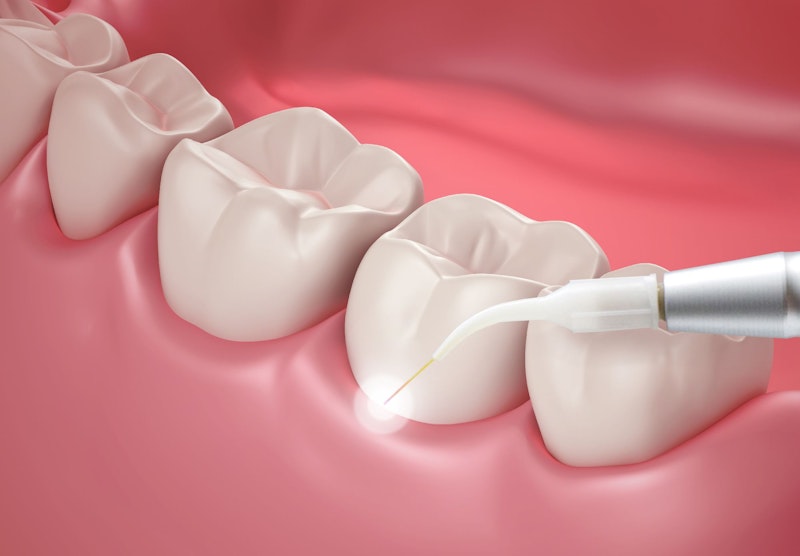
Treating Gum Recession:
Gum recession exposes the tooth roots, which can lead to sensitivity, decay, and even tooth loss.Treating Advanced Gum Disease:
In advanced stages of gum disease, surgery is essential to clean infections and restore damaged tissue.Enhancing Smile Aesthetics:
Gum surgery can be performed to correct the gum line and improve the appearance of the smile.
Appointment Booking
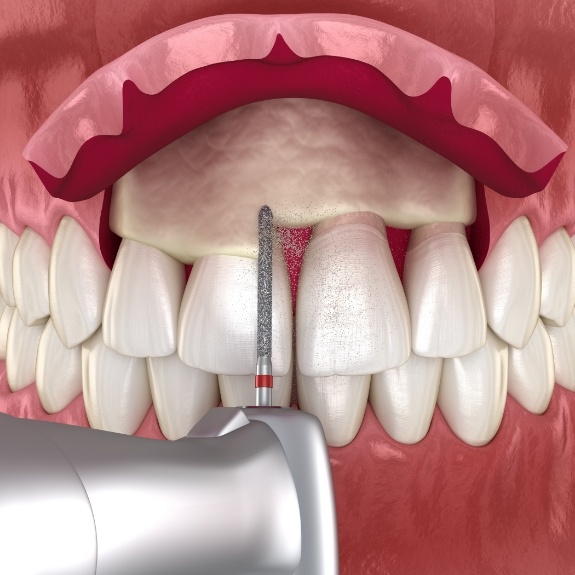
Types of Gum Surgery
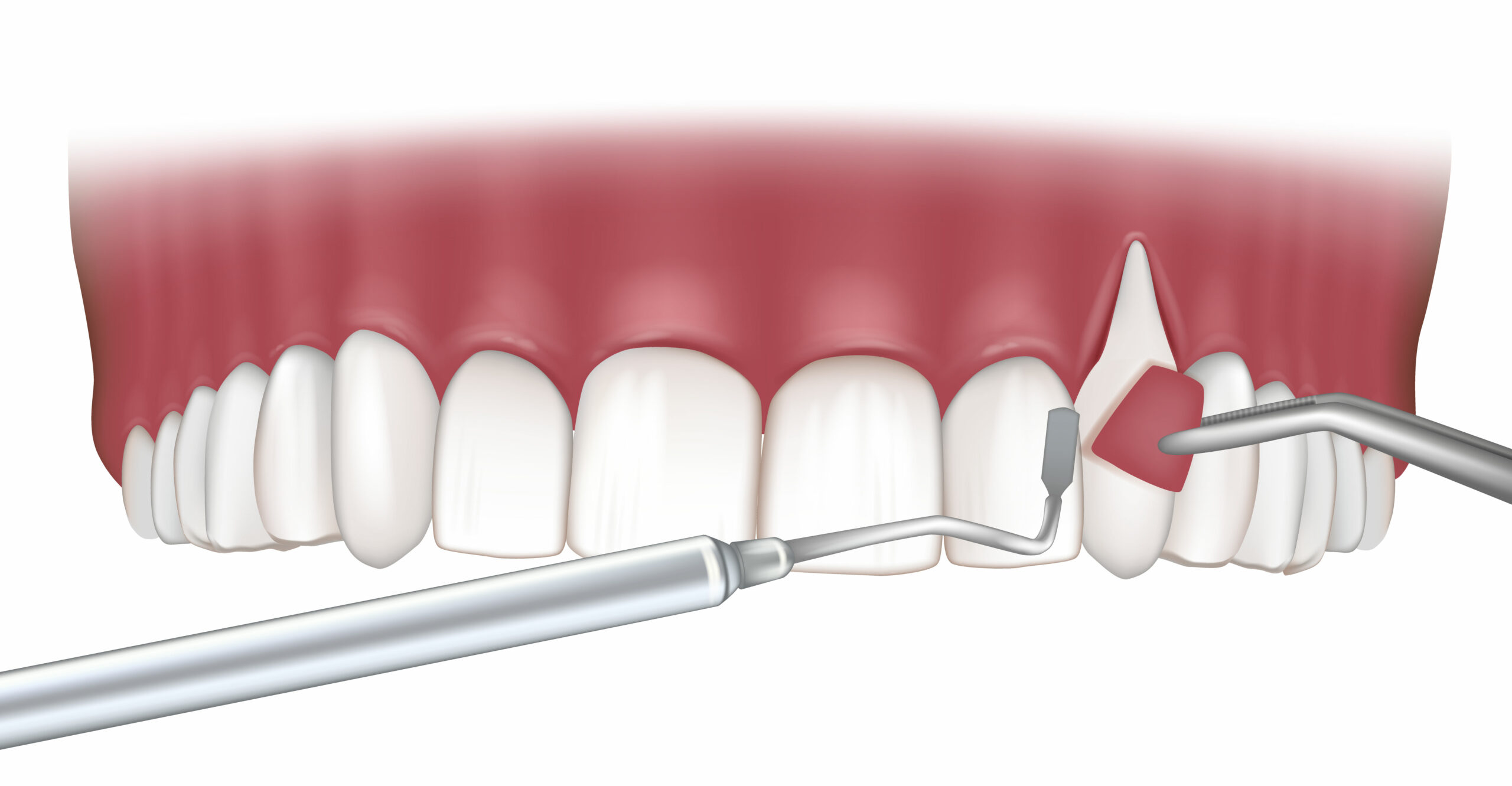
Gum Graft Surgery:
- Purpose: Treat gum recession and cover exposed tooth roots.
- Procedure: Gum tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth or alternative sources and grafted onto the recessed area.
- Benefits: Reduces sensitivity, improves aesthetics, and prevents further gum recession.
Flap Surgery:
- Purpose: Deep cleaning beneath the gums to remove plaque and hardened tartar.
- Procedure: Gums are cut and lifted back to allow access to the roots and underlying bone.
- Benefits: Reduces inflammation and prevents progression of gum disease.
Gingivectomy (Cosmetic Gum Surgery):
- Purpose: Reshape the gum line and remove excess gum tissue to improve the appearance of the teeth.
- Benefits: Ideal for individuals with a gummy smile.
Bone and Tissue Regeneration Surgery:
- Purpose: Restore bone and tissue lost due to gum disease.
- Procedure: Uses regenerative materials such as bone grafts or special membranes.
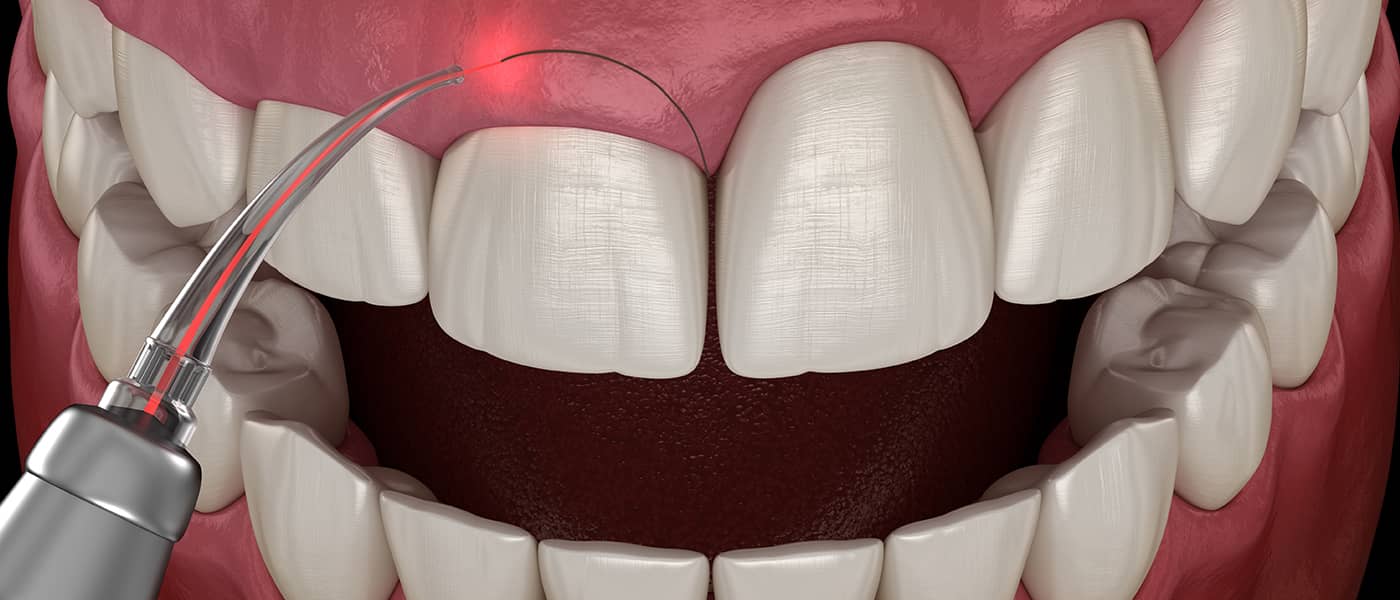
Benefits of Gum Surgery
Improved Oral Health:
Gum surgery helps eliminate infections and plaque, enhancing overall oral health.Prevention of Further Gum Recession:
By rebuilding gum tissue, it prevents further recession and potential tooth loss.Reduced Tooth Sensitivity:
Covering exposed tooth roots reduces sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.Enhanced Smile Appearance:
Correcting the gum line and restoring tissues improves the aesthetics of your smile.
Drawbacks and Limitations of Gum Surgery
Lengthy Recovery Period:
Full recovery may take several weeks to months.Risk of Infection or Bleeding:
Poor oral hygiene may lead to infection or bleeding after surgery.High Cost:
Depending on the type of surgery and techniques used, costs can be significant.Temporary Tooth Sensitivity:
Teeth may become temporarily sensitive after the procedure.
Post-Operative Care for Gum Surgery
To ensure faster recovery and prevent complications, follow these essential tips:
Maintain Oral Hygiene:
Use a soft toothbrush and dentist-recommended mouthwashes.Avoid Hard and Spicy Foods:
Stick to soft and cool foods like yogurt and smoothies.Use Cold Compresses:
Apply cold compresses to reduce swelling and inflammation.Visit Your Dentist:
Schedule follow-up appointments to monitor recovery and remove stitches (if necessary).
Who Are Suitable Candidates for Gum Surgery?
Gum surgery is ideal for individuals who:
- Are suffering from gum recession or advanced gum diseases.
- Seek to improve the appearance and aesthetics of their smile.
- Have good general health and do not smoke.
- Can maintain proper oral hygiene habits.
Cost of Gum Surgery
The cost of gum surgery depends on various factors, including:
- Type of Surgery Required: (e.g., gum grafting, flap surgery, etc.)
- Extent of Gum and Tooth Damage:
- Dentist’s Expertise and Experience:
- Geographic Location of the Clinic:
For precise cost details, it’s best to consult your dentist directly.

